Expendable Launch System
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 

An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are either destroyed during reentry or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of several rocket stages that are discarded sequentially as their fuel is exhausted and the vehicle gains altitude and speed. As of 2022, most satellites and human spacecraft are currently launched on ELVs. ELVs are simpler in design than reusable launch systems and therefore may have a lower production cost. Furthermore, an ELV can use its entire fuel supply to accelerate its payload, offering greater payloads. ELVs are proven technology in widespread use for many decades.[1]
Current operators
Arianespace
China
ISRO
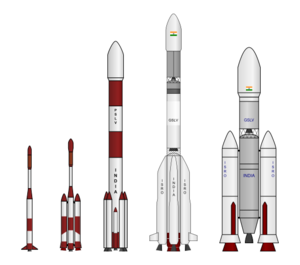
During the 1960s and 1970s, India initiated its own launch vehicle program in alignment with its geopolitical and economic considerations. In the 1960s–1970s, the country India started with a sounding rocket in the 1960s and 1970s and advanced its research to deliver the Satellite Launch Vehicle-3 and the more advanced Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV), complete with operational supporting infrastructure by the 1990s.[2]
JAXA
Roscosmos
United States
Several governmental agencies of the United States purchase ELV launches. NASA is a major customer with the Commercial Resupply Services and Commercial Crew Development programs, also launching scientific spacecraft. The vast majority of launch vehicles for its missions, from the Redstone missile to the Delta, Atlas, Titan and Saturn rocket families, have been expendable. As its flagship crewed exploration replacement for the partially reusable Space Shuttle, NASA's newest ELV, the Space Launch System flew successfully in November 2022 after delays of more than six years. It is planned to serve in a major role on crewed exploration programs going forward.[3][4]
The United States Air Force is also an ELV customer, having designed the Titan, Atlas, and Delta families. Both the Delta IV and Atlas V from the 1994 Evolved ELV (EELV) program remain in active service, operated by the United Launch Alliance.[5] The National Security Space Launch (NSSL) competition has selected two EELV successors, the expendable Vulcan Centaur and partially reusable Falcon 9, to provide assured access to space.[6]
Iranian Space Agency
Safir
Simorgh
Qoqnoos
Israel Space Agency
See also
- Comparison of orbital launch systems
- Comparison of orbital launchers families
- Launch vehicle
- Lists of rockets
- Spacecraft propulsion
- Spaceflight
References
- ↑ "Expendable Launch Vehicles". http://spacetethers.com/elv.html.
- ↑ Gupta, S.C.; Suresh, B.N.; Sivan, K. (2007). "Evolution of Indian launch vehicle technologies". Current Science (Bangalore: Indian Academy of Sciences) 93 (12): 1697. http://www.currentscience.ac.in/Downloads/article_id_093_12_1697_1714_0.pdf. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ↑ Gebhardt, Chris; Burghardt, Thomas (2022-11-16). "SLS makes successful debut flight, sending Artemis I to the Moon" (in en-US). https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2022/11/artemis-i-launch-nov/.
- ↑ "NASA Prepares Rocket, Spacecraft Ahead of Tropical Storm Nicole, Re-targets Launch". NASA. 8 November 2022. https://blogs.nasa.gov/artemis/2022/11/08/nasa-prepares-rocket-spacecraft-ahead-of-tropical-storm-nicole-re-targets-launch/.
- ↑ Boeing, Lockheed Martin to Form Launch Services Joint Venture | SpaceRef - Your Space Reference
- ↑ Erwin, Sandra (7 August 2020). "Pentagon picks SpaceX and ULA to remain its primary launch providers". SpaceNews. https://spacenews.com/pentagon-picks-spacex-and-ula-to-launch-national-security-satellites-for-next-five-years/.
External links
- ULA website
- Arianespace website
- ESA website
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries website
 |
Categories: [Expendable space launch systems]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/18/2024 03:33:58 | 10 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Engineering:Expendable_launch_system | License: CC BY-SA 3.0


 KSF
KSF