Phase Separation
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki
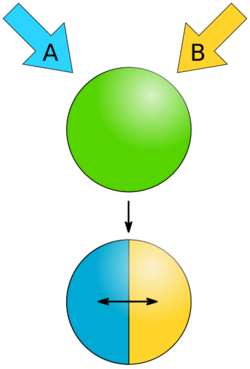

Phase separation is the creation of two distinct phases from a single homogeneous mixture.[1] The most common type of phase separation is between two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water. This type of phase separation is known as liquid-liquid equilibrium. Colloids are formed by phase separation, though not all phase separations forms colloids - for example oil and water can form separated layers under gravity rather than remaining as microscopic droplets in suspension.
Phase separation in cold gases
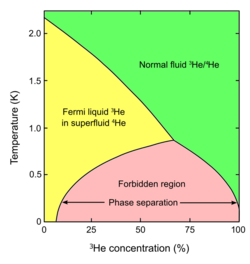
A mixture of two helium isotopes (helium-3 and helium-4) in a certain range of temperatures and concentrations separates into parts. The initial mix of the two isotopes spontaneously separates into [math]\ce{ ^{4}He }[/math]-rich and [math]\ce{ {}^3He }[/math]-rich regions.[2] Phase separation also exists in ultracold gas systems.[3] It has been shown experimentally in a two-component ultracold Fermi gas case.[4][5] The phase separation can compete with other phenomena as vortex lattice formation or an exotic Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov phase.[6]
See also
- Biomolecular condensate
- Colloid
- Phase diagram
- Spinodal decomposition
- Cahn–Hilliard equation
References
- ↑ "Phase separation". IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the "Gold Book") (2nd ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications. 1997. doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04534. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8. https://goldbook.iupac.org/html/P/P04534.html.
- ↑ Pobell, Frank (2007). Matter and methods at low temperatures (3rd rev. and expanded ed.). Berlin: Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-46356-6. OCLC 122268227.
- ↑ Carlson, J.; Reddy, Sanjay (2005-08-02). "Asymmetric Two-Component Fermion Systems in Strong Coupling". Physical Review Letters 95 (6): 060401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.060401. PMID 16090928. Bibcode: 2005PhRvL..95f0401C.
- ↑ Shin, Y.; Zwierlein, M. W.; Schunck, C. H.; Schirotzek, A.; Ketterle, W. (2006-07-18). "Observation of Phase Separation in a Strongly Interacting Imbalanced Fermi Gas". Physical Review Letters 97 (3): 030401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.030401. PMID 16907486. Bibcode: 2006PhRvL..97c0401S.
- ↑ Zwierlein, Martin W.; Schirotzek, André; Schunck, Christian H.; Ketterle, Wolfgang (2006-01-27). "Fermionic Superfluidity with Imbalanced Spin Populations" (in en). Science 311 (5760): 492–496. doi:10.1126/science.1122318. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 16373535. Bibcode: 2006Sci...311..492Z.
- ↑ Kopyciński, Jakub; Pudelko, Wojciech R.; Wlazłowski, Gabriel (2021-11-23). "Vortex lattice in spin-imbalanced unitary Fermi gas". Physical Review A 104 (5): 053322. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.104.053322. Bibcode: 2021PhRvA.104e3322K.
Further reading
- Khabibullaev, Pulat K.; Saidov, Abdulla (April 2013). Phase Separation in Soft Matter Physics: Micellar Solutions, Microemulsions, Critical Phenomena. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. ISBN 978-3-662-09278-1.
 |
Categories: [Equilibrium chemistry] [Solvents] [Condensed matter physics]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/21/2024 03:21:35 | 16 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Phase_separation | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF