Calcium Titanate
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 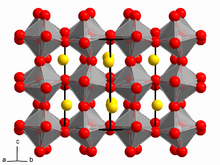
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
calcium titanium oxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula
|
CaTiO3 |
| Molar mass | 135.943 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 4.1 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,975 °C (3,587 °F; 2,248 K) |
| Boiling point | 3,000 °C (5,430 °F; 3,270 K) |
Solubility in water
|
insoluble |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
>1200 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S |
93.64 J/mol·K [1] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-1660.630 kJ/mol [1] |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚)
|
-1575.256 kJ/mol [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Calcium titanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CaTiO3. As a mineral, it is called perovskite, named after Russian mineralogist, L. A. Perovski (1792-1856). It is a colourless, diamagnetic solid, although the mineral is often coloured owing to impurities.
Synthesis
CaTiO3 can be prepared by the combination of CaO and TiO2 at temperatures >1300 °C. Sol-gel processes has been used to make a more pure substance, as well as lowering the synthesis temperature. These compounds synthesized are more compressible due to the powders from the sol-gel process as well and bring it closer to its calculated density (~4.04 g/ml).[2]
Structure
Calcium titanate is obtained as orthorhombic crystals, more specifically perovskite structure.[3] In this motif, the Ti(IV) centers are octahedral and the Ca2+ centers occupy a cage of 12 oxygen centres. Many useful materials adopt related structures, e.g. barium titanate or variations of the structure, e.g. yttrium barium copper oxide.[citation needed]
Applications
Calcium titanate has relatively little value except as one of the ores of titanium, together with several others. It is reduced to give titanium metal or ferrotitanium alloys.[4]
See also
- Perovskite
- Perovskite (structure)
- Perovskite solar cell
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Robie, R. A.; Hemmingway, B. S.; Fisher, J. R. (1978). "Thermodynamic properties of minerals and related substances at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure and at higher temperature". Geol. Surv. Bull.: 1452. doi:10.3133/b1452. Bibcode: 1978BUSGS.....1452R. https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc1114954/m2/1/high_res_d/report.pdf.
- ↑ Dunn, Bruce; Zink, Jeffrey I. (September 2007). "Sol–Gel Chemistry and Materials". Accounts of Chemical Research 40 (9): 729. doi:10.1021/ar700178b. PMID 17874844.
- ↑ Buttner, R. H.; Maslen, E. N. (1 October 1992). "Electron difference density and structural parameters in CaTiO3". Acta Crystallographica Section B 48 (5): 644–649. doi:10.1107/S0108768192004592.
- ↑ Sibum, Heinz; Güther, Volker; Roidl, Oskar; Habashi, Fathi; Wolf, Hans Uwe (2000). "Titanium, Titanium Alloys, and Titanium Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_095. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
External links
- Crystal structure of CaTiO3
 |
Categories: [Calcium compounds] [Titanates] [Perovskites]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 01/28/2025 07:47:11 | 9 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Calcium_titanate | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF