Emde Degradation
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki | Emde degradation | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Hermann Emde |
| Reaction type | Degradation reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000147 |
The Emde degradation (also called Emde-reaction or Emde-reduction) is a method for the reduction of a quaternary ammonium cation to a tertiary amine with sodium amalgam:[1][2][3]
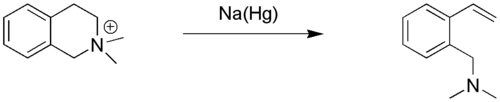
This organic reaction was first described in 1909 by the German chemist Hermann Emde and was for a long time of great importance in structure elucidation of many alkaloids, for example that of ephedrine.
Alternative reducing agents exist for this reaction; for instance, lithium aluminium hydride.
See also
- Related reactions are the Hofmann elimination and the von Braun reaction
References
- ↑ Emde, Hermann (1909). "Spaltung quartärer Ammoniumsalze durch nascierenden Wasserstoff". Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 42 (2): 2590–2594. doi:10.1002/cber.190904202169. https://zenodo.org/record/1426345.
- ↑ Pötsch, W. (1989). Lexikon bedeutender Chemiker. VEB Bibliographisches Institut Leipzig. ISBN 3817110553.
- ↑ Smith, M. B.; March, J. (2001). March's Advanced Organic Chemistry. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-58589-0.
 |
Categories: [Organic redox reactions] [Name reactions] [Degradation reactions]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 07/30/2024 08:48:19 | 9 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Emde_degradation | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
✘
ZWI is not signed. [what is this?]

 KSF
KSF