Solid (State Of Matter)
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki A solid is one of the main states of matter. Solids are made up of atoms or molecules that only move within a very small range in relation to one another.
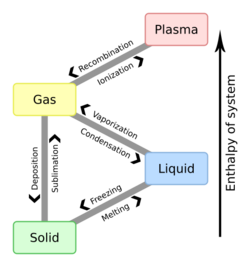
Some solids can vapourize directly into a gas. This is called sublimation. Examples of this are dry ice becoming carbon dioxide gas, and ice disappearing without melting.
Some of the properties of a solid are bulk modulus,which is a measure of how a solid responds to deformation, hardness, which is a measure of how a solid resists abrasion, and melting point, which is the temparature at which a solid becomes a liquid.
Solids at their respective melting point change to liquids.
A crystaline solid has atoms or molecules aranged in a regular repeated pattern and may abruptly change phase as the temperature changes.
An amorphous solid is an apparently solid substance that does not abruptly change its phase as its temperature changes. The atoms or molecules in it are aranged randomly.
Solid measures
Quantities of liquids are measured in units of volume, such as the cubic metre (m³), and mass, such as the kilogram (kg).
See also
Categories: [Condensed matter physics] [Mass] [Volume] [Mass]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/29/2024 22:31:47 | 23 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Solid_(state_of_matter) | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF